Cloud virtualization
Virtualization is running multiple virtual instances on top of a physical computer system using an abstract layer sitting on top of actual hardware. More commonly, virtualization refers to the practice of running multiple operating systems on a single computer at the same time. Applications running on virtual machines are oblivious that they are not running on a dedicated machine. These applications are unaware that they share resources with other applications on the same physical machine.A hypervisor is a computing layer that enables multiple operating systems to execute in the same physical compute resource. These operating systems running on top of these hypervisors are Virtual Machines (VMs) – a component that can emulate a complete computing environment using only software but as if it was running on bare metal. Hypervisors, also known as Virtual Machine Monitors (VMMs), manage these VMs while running side by side. A hypervisor creates a logical separation between VMs. It provides each of them with a slice of the available compute, memory, and storage resources.It allows VMs not to clash and interfere with each other. If one VM crashes and goes down, it will not make other VMs go down with it. Also, if there is an intrusion in one VM, it is fully isolated from the rest.
Definition of the cloud
Let’s now attempt to define cloud computing.The cloud computing model offers computing services such as compute, storage, databases, networking, software, machine learning, and analytics over the internet and on-demand. You generally only pay for the time and services you use. Most cloud providers can provide massive scalability for many of their services and make it easy to scale services up and down.As much as we tried to nail it down, this is still a pretty broad definition. For example, we specify that the cloud can offer software in our definition. That’s a pretty general term. Does the term software in our definition include the following?
- Video Conferencing
- Virtual desktops
- Email services
- Contact Center
- Document Management
These are just a few examples of what may or may not be included as available services in a cloud environment. When it comes to AWS and other major cloud providers, The answer is yes. When AWS started, it only offered a few core services, such as compute (Amazon EC2) and basic storage (Amazon S3). As of 2022, AWS has continually expanded its services to support virtually any cloud workload. Currently, It has more than 200 fully featured services for compute, storage, databases, networking, analytics, machine learning, artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), mobile, security, hybrid, virtual & augmented reality (VR and AR), media, application development, and deployment. As a fun fact, as of 2021, Amazon Elastic Cloud Compute (EC2) alone offers over 475 types of compute instances.For the individual examples given here, AWS offers the following:
- Video conferencing – Amazon Chime
- Virtual desktops – AWS Workspaces
- Email services – Amazon WorkMail
- Contact Center – Amazon Connect
- Document Management – Amazon Workdocs
As we will see throughout the book, here is a sample of AWS’s offers many services. Additionally, since it was launched, AWS services and features have grown exponentially every year, as shown in the following figure:
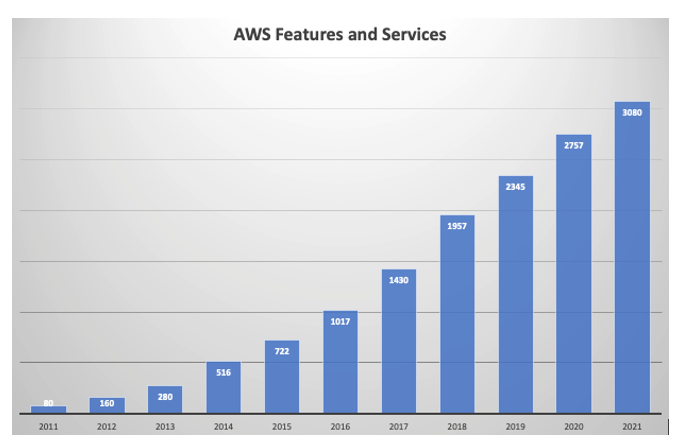
Figure 1.1 – AWS – number of features
There is no doubt that the number of offerings will continue to grow at a similar rate for the foreseeable future. AWS is a cloud market leader as it has a lot of functionality. They are innovating faster, especially in new areas such as Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence, the Internet of Things, Serverless Computing, Blockchain, and even quantum computing.You must have heard cloud terms more often in different contexts, including the public and private clouds. Let’s learn more about it.
